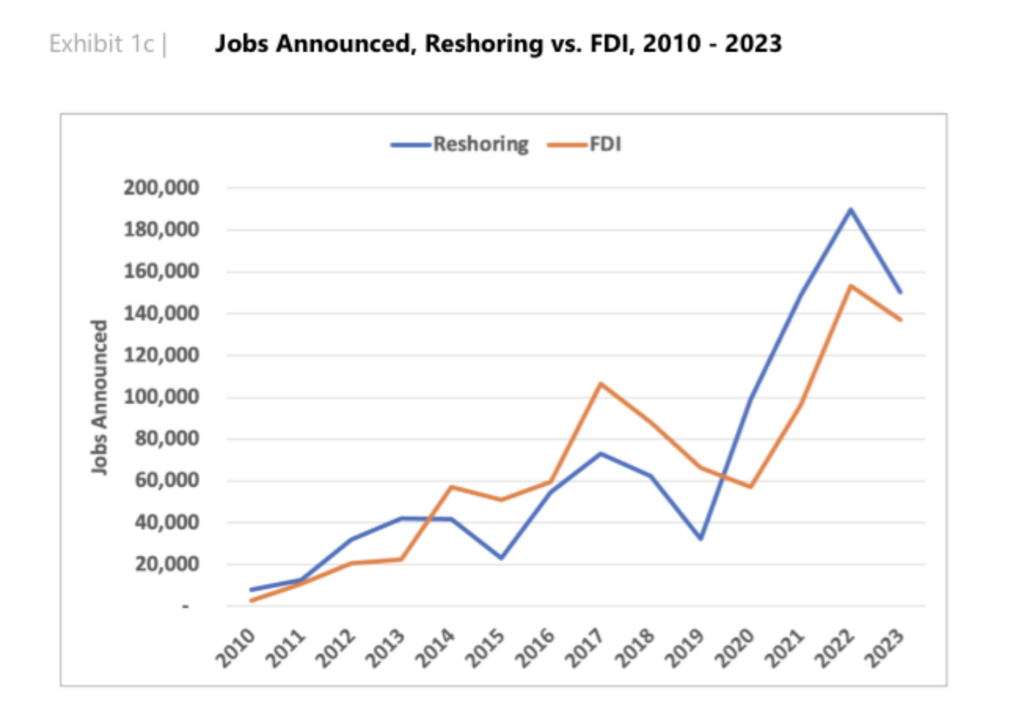
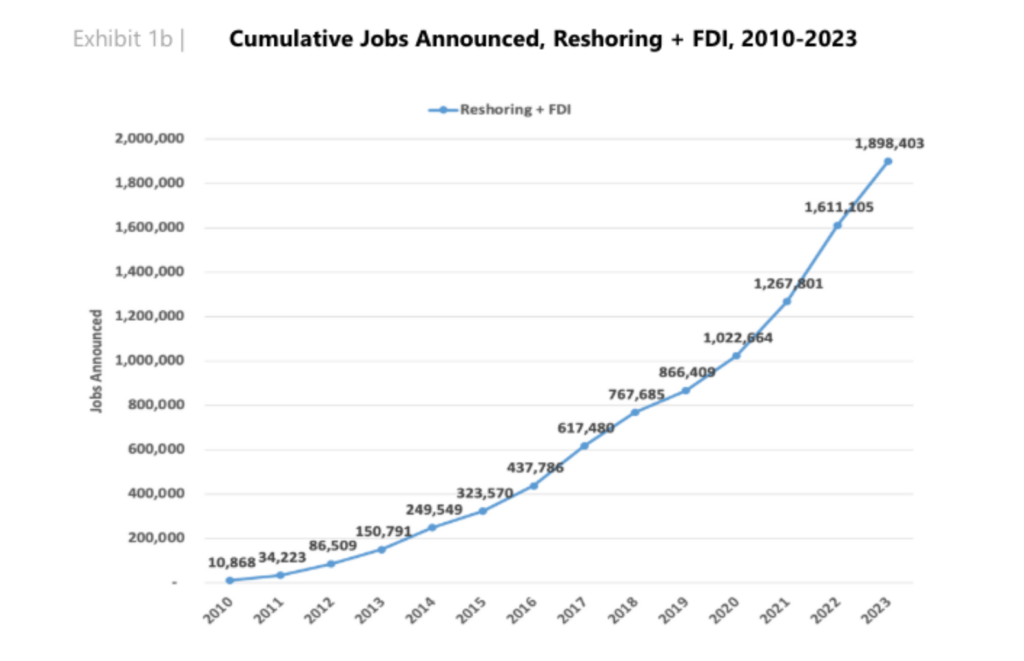
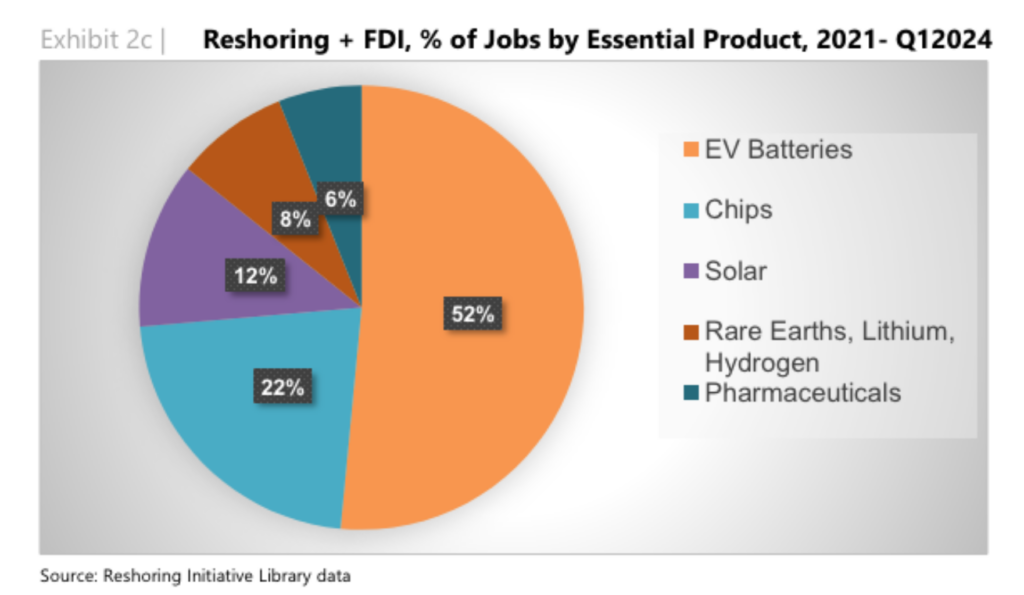
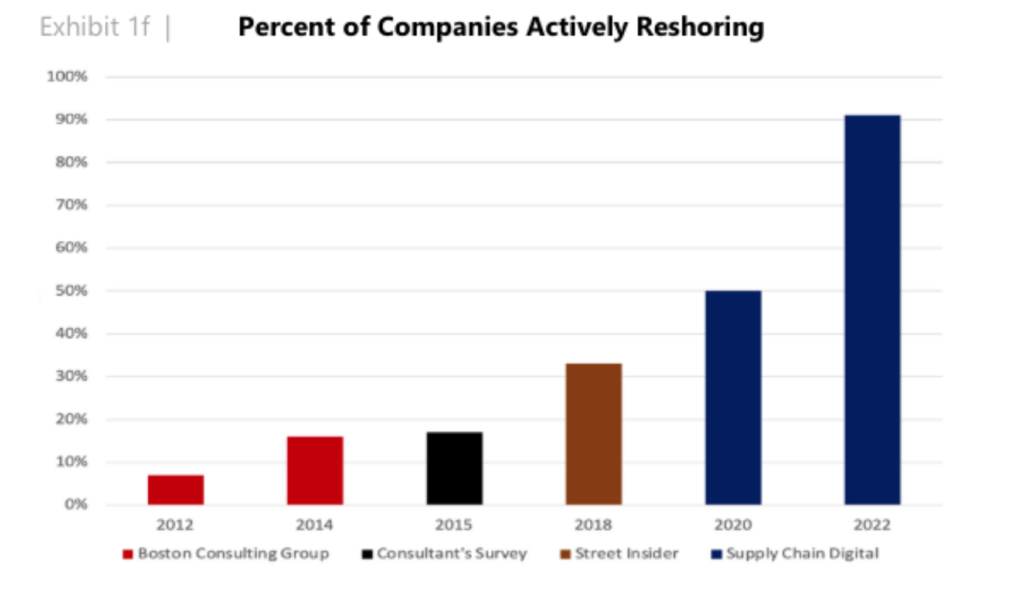
Reshoring trends have become a significant force in the manufacturing and supply chain sectors, bringing substantial benefits to the economy. This shift, driven by various factors, is creating a record number of jobs in 2024. Let's explore the impact of reshoring trends on job creation and the broader implications for businesses and workers.
The Reshoring Revolution
Reshoring refers to the process of bringing manufacturing and production activities back to the home country from overseas. This reshoring trend has gained momentum due to several key factors:
Supply Chain Disruptions: The COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, prompting companies to reconsider their offshore operations.
Rising Costs Abroad: Increasing labor and production costs in traditionally low-cost countries have made reshoring more attractive.
Government Incentives: Various government policies and incentives encourage companies to bring operations back home.
Consumer Preferences: Growing consumer demand for locally-made products is driving companies to relocate manufacturing.
Record Job Creation
The impact of reshoring on job creation cannot be overstated. According to recent reports, reshoring is responsible for creating a record number of jobs in 2024. This surge in employment is due to several reasons:
New Manufacturing Facilities: Companies are investing in new manufacturing plants and facilities, creating numerous job opportunities.
Reopening Closed Plants: Some businesses are reopening previously shuttered factories, bringing jobs back to local communities.
Skilled Labor Demand: The need for skilled labor in advanced manufacturing processes is driving employment growth.
Geopolitical Risk and Reshoring
Geopolitical risks have played a significant role in accelerating the reshoring trends. The Reshoring Initiative's 2023 Annual Report highlights how geopolitical tensions, such as trade wars and international conflicts, have prompted companies to reduce dependency on foreign manufacturing. The desire to mitigate risks associated with geopolitical instability has led many businesses to relocate production back to their home countries. This strategic move ensures more stable and predictable supply chains, crucial for maintaining business continuity (Reshoring Initiative) (SEAMS).
Europe: Russia’s attack on Ukraine has driven Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) from Europe to the U.S. due to the availability and pricing of natural gas and electricity. The trend in reshoring and FDI from Europe is increasing again after a dip during the pandemic years. In 2021 and 2022, European origin cases constituted 13% of the total jobs announced, compared to 34% in 2023 and a projected 37% in 2024 (Reshoring Initiative).
Israel: The October 7 Hamas attack occurred too late in 2023 to impact that year's data significantly. However, it is anticipated to have a ripple effect across various industries, causing broad economic and supply chain disruptions that will influence costs, material availability, and production schedules (Reshoring Initiative).
Taiwan: U.S.-China tensions have been mounting for several years, leading many geopolitical and corporate strategists to anticipate reshoring as a form of insurance against future conflicts (Reshoring Initiative).
China: China faces the highest combination of trade dependency, single sourcing, and geopolitical risk. Reshoring and FDI from China are near historical highs, with reshoring alone at an all-time high of 87% (Reshoring Initiative).
Economic and Social Benefits
Reshoring trends offer numerous benefits beyond job creation:
Economic Growth: Increased manufacturing activities stimulate local economies, leading to higher GDP and improved living standards.
Community Revitalization: The reopening of factories and new job opportunities revitalizes communities, reducing unemployment rates and increasing social stability.
Innovation and Competitiveness: Reshoring fosters innovation by bringing production closer to R&D centers, enhancing collaboration and accelerating product development.
Challenges and Considerations
While reshoring trends present significant advantages, they also come with challenges that companies must address:
Initial Costs: Setting up new manufacturing facilities or upgrading existing ones can be costly.
Supply Chain Adjustments: Businesses need to reconfigure their supply chains to accommodate domestic production.
Skilled Labor Shortage: Finding and training skilled workers for advanced manufacturing roles can be challenging.
The Future of Reshoring
The reshoring trends are expected to continue growing in the coming years. Companies are likely to invest more in domestic production capabilities, driven by the desire for supply chain resilience, cost-effectiveness, and consumer preferences. The ongoing support from government policies and incentives will further bolster reshoring trends.
Conclusion
Reshoring is transforming the manufacturing landscape, creating record numbers of jobs, and revitalizing local economies. As companies navigate the challenges and embrace the opportunities presented by reshoring, the long-term benefits for businesses, workers, and communities will continue to unfold. The future of reshoring looks promising, with the potential to drive sustainable economic growth and innovation.
This article emphasizes reshoring trends and their significant impact on job creation and economic growth in 2024. By incorporating geopolitical risks, challenges, and future outlooks, it provides a comprehensive and engaging overview of the reshoring phenomenon.